Dynamic PDO Mappings
Dynamic PDO mapping allows for customizing the PDOs to fit customer needs. As there is no performance impact to using dynamic mapping vs fixed mapping and it allows for greater flexibility, dynamic mapping is preferred over using the fixed maps when possible. Some EtherCAT![]() EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs masters may be unable to use dynamic mappings.
EtherCAT is an open, high-performance Ethernet-based fieldbus system. The development goal of EtherCAT was to apply Ethernet to automation applications which require short data update times (also called cycle times) with low communication jitter (for synchronization purposes) and low hardware costs masters may be unable to use dynamic mappings.
Objects available for PDO mappings are listed in the object dictionary table.
Restrictions of dynamic mapping:
- Depending on the desired cycle time, PDO sizes are limited to the following:
- 1ms and faster: 14 total mapped objects in each direction
- 2ms and slower: 30 total mapped objects in each direction
- Up to 30 objects per PDO are permitted if the above limits are followed
To configure dynamic maps:
- Clear the mapping selection to enable it to be changed (write 0 to object 1C12h sub 0 and 1C13h sub 0)
- Objects can be mapped to 1600-1603h for drive outputs and 1A00-1A03h for inputs. Each index is a separate PDO.
- Write 0 to sub-index 0 to clear the PDO map and permit updating
- Write each following sub-index with the desired object entry
- Write the number of objects back to sub-index 0 to complete the mapping
- If any objects are not PDO mappable, an error will be received
- Write 1C12h sub 1 to 4 with the PDOs (1600h-1603h) that should be used in receive direction of the drive (set point values).
- Write 1C13h sub 1 to 4 with the PDOs (1A00h-1A03h) that should be used in transmit direction of the drive (actual values).
- Write 1C12h sub 0 and 1C13h sub 0 with the number of mapped PDOs that were setup.
Padding
The AKD2G uses byte alignment on PDOs. If more than byte alignment is required, padding objects can be inserted into PDO maps. This is achieved by mapping index 0000h sub 0 and specifying the size. For example, setting a PDO entry with 00000010h will assign 16 bits of padding (2 bytes) and 00000008h will assign 8 bits of padding (1 byte). The smallest amount of padding allowed is 1 byte.
TwinCAT 3 Dynamic PDO Example
The cyclic data is visible in the PDO-assignment window for the Inputs and Outputs of the Sync Managers. The default PDO settings use the dynamic PDOs 1600h/1A00h for axis 1 and on dual axis drives 1601h/1A01h are mapped for axis 2 with the objects necessary for cyclic synchronous position mode control.
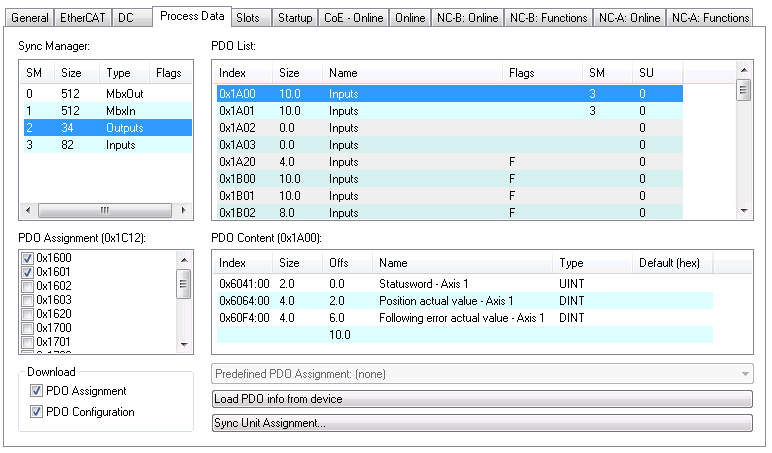
The PDO maps can be changed by selecting the desired PDO and right clicking in the PDO content window. Existing entries can be changed or deleted, and new entries can be inserted between existing or appended to the end.
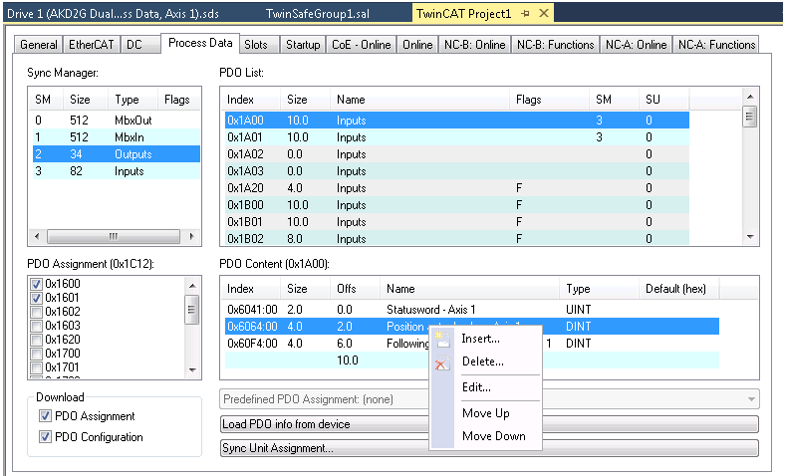
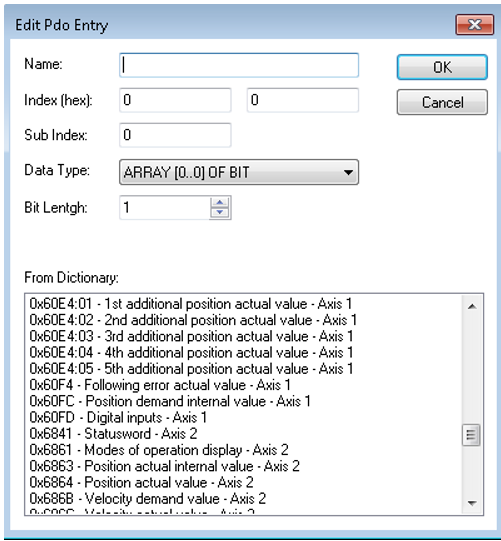
A list of mappable objects is shown. The list only shows objects that can be mapped in the direction of the map being changed. For example, attempting to insert an object on the input PDO 1A00h only shows objects that can be mapped in the direction from the drive to the controller, as shown below
As the PDO map is changed, the startup script is automatically updated by TwinCAT to send to the drive during the PREOP to SAFEOP transition.
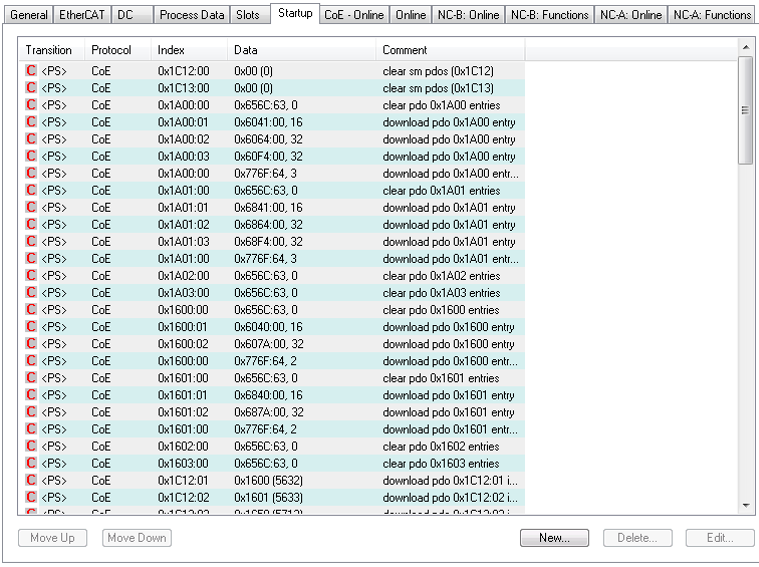
The meaning of the data (for example 0x60410010 in the mapping of 0x1A00 sub 1) is as follows:
- 0x6041 is the index of the DS402 statusword.
- 0x00 is the sub-index of the DS402 statusword.
- 0x10 is the number of bits for this entry, ie. 16 bits or 2 bytes.






